PPPoE MTU Explained
PPPoE MTU is a buzz word that many people ask about even if they don't have anything to do with network engineering. Just being a broadband subscriber with a PPPoE circuit is enough to get introduced to the concept.
In this post I will be explaining how PPPoE MTU is calculated and what is the default value. Therefore I would expect the reader to be familiar with what MTU is and with What PPPoE is.
PPPoE MTU:
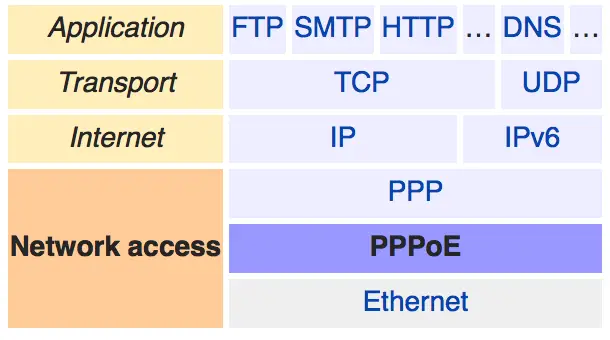
PPPoE MTU defines the maximum number of bytes that a PPPoE payload can have. This typically starts from IP layer in most cases. Below is what a typical PPPoE packet look like in terms of headers. Ethernet, then PPPoE then PPP followed by IP or IPv6 payload.
PPPoE MTU calculation = Interface MTU - Ethernet header (14 bytes) - PPPoE (6 bytes) - PPP (2 bytes)
The only variable in the above calculation is going to be the interface MTU setting, which defaults to 1514 as per the outputs below on a Juniper MX box with a GE interface.
This would give us the famous default value of 1492 bytes on most of standard equipment in the market. The value can be manipulated through configuration but it has to be manipulated over the complete path from the CPE to the BNG to avoid problems.
triton@neptune>show interfaces ge-4/1/8
Physical interface: ge-4/1/8, Enabled, Physical link is Down
Interface index: 182, SNMP ifIndex: 693
Link-level type: Ethernet, MTU: 1514, Speed: 1000mbps, BPDU Error: None,
Device flags : Present Running Down
---- output ommitted ----
You can use this MTU (header overhead) calculator to calculate the PPPoE MTU or any other value based on specific setup requirements. Give it a try.